Posts Tagged ‘OSC’
Thursday, October 10th, 2013

On June 15, 2012, President Obama signed a memo calling for deferred action for certain undocumented young people who came to the U.S. as children and have pursued education or military service here. Applications under the program which is called Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (“DACA”) began on August 15, 2012. Individuals that meet particular criteria, are awarded employment authorization (a/k/a an “EAD Card”) by USCIS.
USCIS does not alert employers when EAD cards have been issued to existing employees, and the employee is under no obligation to present the document to the employer. However, should they do so, the employer is obligated to examine the document.
The Attached Fact Sheet identifies the employer’s obligations during the Form I-9 process and provides specific guidance to employers on the treatment of EADs issued by USCIS to DACA recipients, whether they be current employees who come forward on their own, or new hires.
Note that DACA guidance does not direct employers to perform E-Verify queries on current employees who present DACA work authorization. Rather, it states that employers should complete a new Form I-9 and perform an E-Verify query in certain situations involving material changes to identity information. More on this topic can be found in the new M-274 Handbook on pages 23-24.
Should you like to become a client of our office or have particular questions pertaining to this topic, please feel free to contact us.
Tags: DACA, DACA EAD Cards, DACA Fact Sheet, DOL, E-Verify, EAD Employment Authorization, I-9 AUDIT, I-9 Form, I-9 Reverification, I-9 Training, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, M-274, OSC, SSA, USCIS
Posted in DACA | DAPA, Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), Department Of Labor (DOL), Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, OSC, Social Security | Comments Off on Form I-9 Processing for DACA Recipients
Sunday, October 6th, 2013
 The Immigration and Nationality Act (“INA”) prohibits employers from discriminating against individuals based on their citizenship or immigration status, or based on their national origin, in the Form I-9 process. It is important for employers to develop, implement and enforce anti-discrimination policies, practices and procedures, and to ensure that all employees conducting Form I-9 verification or E-Verify confirmation understand all program rules. Employers should also provide appropriate and adequate employee education on employer responsibilities and worker rights.
The Immigration and Nationality Act (“INA”) prohibits employers from discriminating against individuals based on their citizenship or immigration status, or based on their national origin, in the Form I-9 process. It is important for employers to develop, implement and enforce anti-discrimination policies, practices and procedures, and to ensure that all employees conducting Form I-9 verification or E-Verify confirmation understand all program rules. Employers should also provide appropriate and adequate employee education on employer responsibilities and worker rights.
To prevent discrimination, employer’s should treat all people equally when
- announcing a job
- taking applications
- performing interviews
- making job offers
- verifying the individual’s authorization to work
- hiring the individual
- terminating the individual’s employment
Employers also must not retaliate against a person who
- files a charge of discrimination with OSC or EEOC
- participates in an investigation or prosecution of a discrimination complaint
- asserts his or her rights or the rights of another person under anti-discrimination laws
The Department of Justice’s Office of Special Counsel for Immigration-Related Unfair Employment Practices (OSC) investigates charges of employment discrimination related to an individual’s citizenship or immigration status or national origin. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) also investigates employment discrimination based on national origin, in addition to other protected bases. OSC investigates national origin claims against employers with four to 14 employees, and EEOC investigates national origin claims against employers with 15 or more employees.
There has been a high level of enforcement by OSC this year concerning the anti-discrimination provision, with three more cases recently publicized in the last month:
- OSC settled with Texas-based Infinity Group who required non-citizens present specific DHS-issued documents such as green-cards or employment authorization to establish identity and employment authorization while similarly not requesting the same of US citizens. They were fined $53,000, had to pay $35K in back pay to those who were damaged as a result of their practices.
- OSC settled with PA-based Huber Nurseries for engaging in citizenship discrimination by preferring to hire temporary H-2A visa holders over Permanent Residents (green-card holders). Huber has agreed to pay $2,250 in civil penalties to the USA and $59,617 in back pay to the six injured parties, who are former refugees; and
- OSC settled with IBM for violating the anti-discrimination provision for placing online job postings for software developers with a preference for F-1 and H-1B visa holders. IBM has agreed to pay $44,400 in civil penalties to the USA.
So, what’s an employer to do?
Employers must accept all documents that are indicated on the List of Acceptable Documents to complete the I-9 form as long as they appear reasonably genuine on their face and relate to the employee. For example, all individuals who possess a driver’s license and unrestricted Social Security card may present those documents to satisfy Form I-9 requirements. Employers may not request or require potential employees to produce “green cards” or United States citizens who look or sound “foreign” to produce birth certificates. The employee chooses which of the acceptable Form I-9 documents to present. Employers must assure that those charged with the responsibility of I-9 management are trained on I-9 regulations and the anti-discrimination provision of the INA – and they must not
- Demand that an employee show specific documents
- Ask to see employment authorization documents before an individual accepts a job offer
- Refuse to accept a document, or refuse to hire an individual, because a document will expire in the future
- Refuse to accept a receipt that is acceptable for Form I-9 purposes
- Demand a specific document when reverifying that an employee is authorized to work
We recommend that you take some time and read the OSC’s Guide to Fair Employment that can be accessed here, that contains some thought provoking What would you do? scenarios that start on page 6.
Should you have questions or require particular guidance on this topic, please feel free to contact our office.
Tags: Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), E-Verify, Employment Practices, Hiring Practices, I-9 Audits, I-9 management, I-9 Penalties, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, ICE Fines, Immigration News, INA Anti-Discrimination Provision, Legal Workforce, OSC, SSA
Posted in Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, OSC, Social Security, USCIS | Comments Off on I-9/E-Verify: Preventing Discrimination in Hiring Practices
Friday, September 27th, 2013

USCIS has indicated that not all SSA documents referring to the ownership of the SSA account or reflecting an application for a new card, are valid receipts for the I-9 process. So, what constitutes a valid SSA replacement receipt?
The only receipt from SSA that is acceptable under the receipt rule is a receipt that states “This is a receipt to show you applied for a social Security Card and the application was for a lost, stolen or damaged document.” Any other receipt would not be acceptable. Your employee may present a receipt for the application for the replacement of any List A, List B, or List C document. The receipt is valid for 90 days. When it expires, the employee must show you the replacement document for which the receipt was given.
After the receipt expires, you should:
1) Cross out the word “receipt” and any accompanying document number
2) Record the number and other required document information from the actual document presented.
3) Initial and date the change.
You cannot accept a receipt for the I-9 Form for an initial or renewal employment authorization, but can accept a receipt for the application for replacement of a lost, stolen or damaged employment authorization document. You cannot accept receipts if employment will last less than three days.
The Three-Day Business Rule
Q: How does an employer that is operational over the weekend but whose HR office (which is open during regular business hours but closed on weekends) count the 3-business days for I-9 purposes?
A: Employers are required to complete the I-9 Form within 3 business days of the employees first day of work for pay. If the business is operational on the weekends, this counts towards the 3 day timeframe for I-9 completion. Thus, in order to remain in compliance for businesses that operate on the weekends, we suggest that the first day of work for pay be on a week day when the HR office representatives who are trained in I-9 procedures are available.
Tags: I-9 Form, I-9 process, I-9 Receipt Rule, I-9 Three-Day Rule, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OSC, Social Security Cards, SSA, USCIS
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, OSC, Social Security, USCIS | Comments Off on I-9 Form Guidance: Social Security Replacement Receipts and the Three Day Business Rule
Tuesday, September 24th, 2013

The question of whether “N/A” may or must be entered in non-applicable fields, or whether N/A is sometimes required and sometimes optional – is a question we’ve all been wondering about. Here’s recent guidance on the topic . . .
If the passport number and country of issuance fields in Section 1 do not apply, the employee MUST write “N/A.” If all else fails, follow the instructions!…In essence that’s the recent guidance – read the instructions when determining if an N/A response is required as it states when an employer or employee may use N/A or must use N/A. Failing to provide a response in a required field may be considered a verification violattion (yes, it’s true!).
Not to belabor it, but this is another very good reason for providing the instructions to the employees when they are filling out Section 1 and deciding which documents to present in the I-9 process. It would be advisable for the employer representative to also have a copy of the instructions on their desk
The I-9 Instructions: http://www.uscis.gov/files/form/i-9.pdf
How have you been dealing with the “N/A” requirement so far? No judgements – let us hear from you.
Tags: Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), I-9 Audits, I-9 Form N/A requirement, I-9 Training, I-9 Violations, I-9/E-Verify News, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OSC, SSA, USCIS
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration Legislation, Immigration News, OSC, USCIS | Comments Off on Part II — Our Continuing Saga of USCIS Answers Concerning the New I-9 Form
Sunday, September 22nd, 2013
 Answers to questions from April 2013 by the American Immigration Lawyer’s Association (AILA) to USCIS Verification Division/Washington, DC re the new I-9 Form, its Instructions, the M-274 Handbook and the I-9 Central website have finally been answered. We will be featuring several of the Q&A’s this week and trust that you will find this both enlightening and informative.
Answers to questions from April 2013 by the American Immigration Lawyer’s Association (AILA) to USCIS Verification Division/Washington, DC re the new I-9 Form, its Instructions, the M-274 Handbook and the I-9 Central website have finally been answered. We will be featuring several of the Q&A’s this week and trust that you will find this both enlightening and informative.
Today, we deal with new name change directives and guidance – Page 23 of the Employer Handbook. In the case of a divorce, it is recommended even where there is no rehire or reverification in order that the employer’s actions are well documented if the government asks to inspect your Forms I-9.
Question: Can USCIS Verification confirm that the only time an employer is required to record a legal name change is in connection with a rehire or reverificaton? In addition, does USCIS intend, by its advice to take steps to be reasonably assured of the employee’s identity and the veracity of the employee’s claim of a legal name change to require female employees to produce marriage licenses or divorce decrees after a change in marital status? To what extent has Verification discussed this change in guidance with OSC or the EEOC to ensure that it is not inconsistent with anti-discrimination provisions?
Answer: Page 24 of the Employer Handbook contains new guidance for employers dealing with a situation where a current employee comes forward with documentation of a new identity. The Handbook states that the employer should complete a new I-9 form, list the original hire date, and provide a written explanation of the circumstances giving rise to the new I-9-. Although we agree that completion of a new I-9 may be the best practice in certain circumstances, requiring employers to complete a new I-9 for existing employees who provide updated identity documentation appears to be at odds with the statute and regulations that require an I-9 only upon “hire.”
The legal basis for the guidance in the Handbook in certain circumstances is based on the INA that refers to the prohibition against continuing to employ an alien knowing that they are unauthorized to work.
An example of this might be presentation to the employer of a new Social Security Card reflecting a new Social Security number and new name which raises material questions as to the identity of the employee, the veracity of information on Form I-9, the genuineness of any documents presented in Section 2 that contain a Social Security number, and the relation of these documents to the person who presented them. The employer can no longer reasonably rely on the Form I-9 to be assured that the individual is authorized to work. In this scenario, USCIS suggests completion of a new Form I-9 to ensure the employee is eligible to continue in employment. This is a suggestion, and not a requirement.
Our office agrees with this position and recommends filling out a new I-9 form. Should you have any questions concerning this guidance, please contact our office at Info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or call 562 612.3996.
Tags: I-9 AUDIT, I-9 Document Examination, I-9 Folrm Name Changes, I-9 Form Instructions, I-9 Form Penalties, I-9 Reverification, I-9 Violations, I-9/-Verify News, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OSC, Social Security, USCIS
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration Legislation, OSC, Social Security, USCIS | Comments Off on USCIS Provides Answers to New I-9 Form Questions
Friday, September 13th, 2013

This gives you a good look at what the OSC is targeting these days.
We’d also like to take the opportunity to remind you to schedule I-9 audits yearly (they don’t have to be full audits – but can be partial) so that you can see what’s buried in your paperwork and catch it before the issues become reoccurring problems AND before ICE knocks on your door. Training: Well, we can’t say enough on training. Employers need to provide ongoing ‘refresher’ training every year. The issues change from year to year as do the interpretations. Lastly, review your policies and procedures in relation to compliance best practices for your business. Make sure they are up to date, and make sure that every employee who is involved with processing I-9 forms participates in yearly training, reads the M-274 Employer Handbook and remembers to provide to every employee a List of Acceptable Documents along with the I-9 form Instructions when they fill out the form. So many errors can be caught at the onset just by reviewing the instructions and the List of Acceptable Documents.
Lastly, our Employer Resource Center is an excellent resource, as is our Blog and our LinkedIn Group, I-9/E-Verify: Smart Solutions for Employers. Sign up and keep yourself informed
Tags: Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), DOL, Employer Compliance News, I-9 Compliance, I-9 Employer Resources, I-9 Policies, I-9 Training, I-9 Violations, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Legal Workforce, OSC, SSA
Posted in Uncategorized | Comments Off on A Sampling of OSC Recent I-9 Enforcement Activities
Thursday, September 5th, 2013

Updated entry re below post: 10/11/2013
In an update to the statements made by ICE to AILA (the American Immigration Lawyer’s Association) in their April 11, 2013 liaison meeting, ICE HSI Worksite Enforcement representatives recently announced to stakeholders that it now has no position on pre-population of Section 1 of the I-9 by electronic I-9 programs, reversing its position from being “not permissible.” This appears to represent an important change from the position the agency announced to AILA and several other organizations in early April that pre-population of Section 1 by electronic I-9 programs is always prohibited.
The AILA Verification and Documentation Liaison Committee will seek clarification of ICE’s recent statements and the impact on employers and electronic I-9 programs at the fall liaison meeting.
::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
ICE HSI (Homeland Security Investigations) directorate strongly spoke out against I-9 pre-population at a recent AILA (American Immigration Lawyers Association) meeting indicating that it was inappropriate and that pre-populating Form I-9 is considered unacceptable practice and a violation. More recently, OSC in a response to a TAL (Technical Assistance Letter), also spoke out against pre-population stating their concern regarding Section 1 containing outdated or incorrect information.
In light of this change in policy, software providers and employers who use electronic I-9 software should consider this most recent announcement. We caution employers to review their hiring procedures as it relates to this compliance issue with their software providers.
For more information on I-9/E-Verify employer compliance, please refer to our employer resource center.
Tags: Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), HSI, I-9 Prepopulation, I-9 Remote Hires, I-9 Software, I-9 Violations, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OSC, Technical Assistance Letters, Workforce Compliance
Posted in Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News | Comments Off on ICE Reverses Position on Pre-Population of Section 1 of I-9 Form
Monday, September 3rd, 2012
By: Timothy Sutton, Communications Editor
 Today, recruiters, human resource managers, and small business owners utilize the Internet to recruit new employees. Online recruiting is cheap, efficient, and reaches a much broader audience than traditional forms of media. While there are numerous advantages to employing a professional staffing agency to locate prospective employees through the Internet, many employers choose to self-publish want ads through popular websites like monster.com or craiglist.org. Self-publishing online job posting gives the employer complete control over when, where, and how long a post will be visible to the public. Ultimately, do-it-yourself recruiting can be personally tailored to suit a particular employer’s needs.
Today, recruiters, human resource managers, and small business owners utilize the Internet to recruit new employees. Online recruiting is cheap, efficient, and reaches a much broader audience than traditional forms of media. While there are numerous advantages to employing a professional staffing agency to locate prospective employees through the Internet, many employers choose to self-publish want ads through popular websites like monster.com or craiglist.org. Self-publishing online job posting gives the employer complete control over when, where, and how long a post will be visible to the public. Ultimately, do-it-yourself recruiting can be personally tailored to suit a particular employer’s needs.
But recruiters beware. The Internet is much more sophisticated than a virtual corkboard. Keywords and phrases in your job listings can be tracked and monitored by government software, then stored in databases. Recently, the Civil Rights Division of the Office of Special Counsel (OSC) released a Best Practices notice for online job posting. Whether this notice foreshadows future litigation over civil rights violations in hiring practices is yet to be determined; regardless, the message is clear, employers need to exercise caution when recruiting online because the OSC is monitoring online want ads.
Immigration laws prohibit the use of discriminatory language regarding U.S. Citizenship, lawful permanent residence, citizenship status, or national origin unless required by law, regulation or executive order. Curiously, the OSC notice was released shortly after a handful of states attempted to curtail the rights of Deferred Action Childhood Arrival qualifiers to obtain state identification (see our previous post here). There is no data revealing any increase in discriminatory language found in online job postings, but a simple keyword search on either monster.com or craigslist.org reveals numerous non-compliant ads. For instance, if the word “citizen” is entered into Craigslist, ads for dishwashers, personal assistants, security guards, and caregivers pop up. Each ad contains some version of the following discriminatory language that the OSC notice clearly forbids pursuant to the Immigration and Nationality Act at § 1324b that prohibits discrimination based on the citizenship status or national origin in the hiring, firing unfair document practices (“document abuse”) during employment eligibility verification process, and retaliation:
- “Only U.S. Citizens”
- “Citizenship requirement”*
- “Only U.S. Citizens or Green Card Holders”
- “H-1Bs Only”
- “Must have a U.S. Passport”
- “Must have a green card”
One explanation presented by the OSC for the common use of such language is the misinterpretation of federal employment laws. Employers are not limited to the recruitment of U.S. citizens. In fact, we recently published an article on the proper method of verifying the legal employment status of refugee/asylees. Due to the complexity of adhering to the legal requirements of recruiting, hiring, and employing individuals in today’s diverse workplace, employers should seek the professional guidance of an attorney. The cost savings and convenience of self-publishing job postings are heavily outweighed by the potential financial penalties and negative publicity of losing an anti-discrimination lawsuit.
Our office has the experience and successful track record necessary to protect the interests of your enterprise. For more information, contact one of our immigration professionals at info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or call 562 612.3996.
Tags: Anti-Discrimination, Anti-Discrimination Lawsuits, Civil Rights Violations, Discriminatory Language, Employer Comopliance Training, HR Professionals, I-9 Form, I-9/E-Verify News, Immigraiton News, Immigration Compliance Group, Internet Recruitment, Legal Workforce, OSC, OSC Best Practices for Job Posting, Recruiters, Recruitment Discrimination, Staffing Agencies, Talent Acquisition, Unfair Employment Practices
Posted in DACA | DAPA, Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, OSC, Staffing Agencies | Comments Off on RECRUITING: Internet Justice – Respecting Civil Rights in Online Recruiting
Thursday, August 16th, 2012
The Department of Justice Office of Public Affairs recently published a press release pertaining to the employment of two refugees resolving allegations that the company discriminated under the anti-discrimination provision of the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA), when it impermissibly delayed the start date of two refugees after requiring them to provide specific Form I-9 documentation. Best Packing’s violations occurred when they required the refugees to supply the company with additional Form I-9 verification documents in excess of the law. The claim alleged that other non-refugee employees were not required to supply documents other than state issued licenses and social security cards.
In two charges filed with the department, the refugees alleged that they were not allowed to begin employment until they produced unexpired, Department of Homeland Security-issued employment authorization documents, despite the fact that they initially presented sufficient documentation for employment eligibility verification purposes. The charging parties had presented unexpired state identification cards and unrestricted Social Security cards. The state ID’s and unrestricted SS cards were deemed insufficient proof of work authorization.
It is necessary for all those charged with Form I-9 processing at your organization to be very familiar with the list of acceptable documents and to have a thorough understanding of the fact that each employee has the right to present a list A document or a combination B plus C document as long as they are acceptable documents, appear to be genuine and represent the employee that is before you.
Under the settlement agreement, Best Packing agreed to pay $4,379 in back pay and comply with all the requirements of the INA. Understanding the Form I-9 requirements for verifying refugee/asylee(s) will prevent your company from falling victim to similar discriminatory hiring practices.
The process by which an employer is required to verify the employment eligibility of a refugee/asylee(s) when presented with documentation other than the above-referenced List B plus List C combination, can be a bit complicated. Let’s review this.
Asylees and Refugees are individuals seeking the protection of the United States due to persecution suffered in the home country based upon: race, religion, nationality, social group, or political ideology. These individuals are authorized to work in the US because of their immigration status. When presented with documentation of asylum or refugee status, it is advisable to be aware of the following in regard to examining the I-9 form and the documents presented:
SECTION 1:
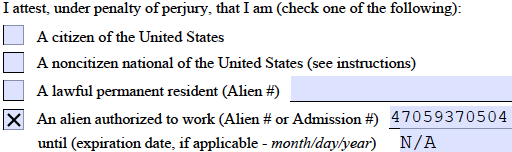
- The employee should check the “An alien authorized to work” box
- Write the I-94 or Alien Registration Number in the first space
- Write “N/A” in the second space, because their employment authorization does not expire
SECTION 2:
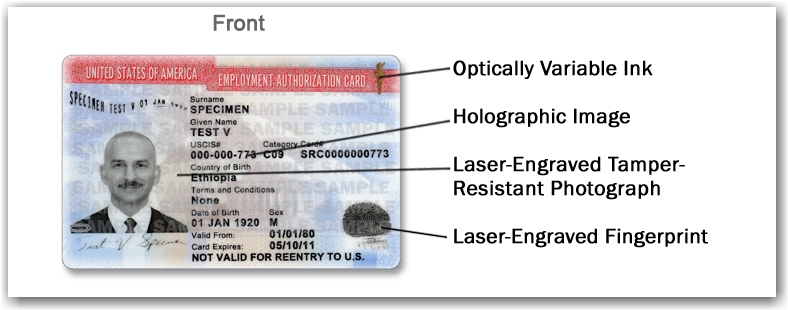
Acceptable Documents are I-94, I-766, or their Employment Authorization Document also known as an EAD card
NOTE: this section presents two different scenarios that require strict attention to time restrictions and combinations of required documents to be presented in order to comply with the USCIS regulations. To complete this section choose from the applicable scenarios below:
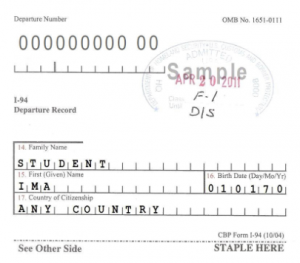
Scenario One: Refugee presents a Form I-94:
When presented with a Form I-94 containing an unexpired refugee admission stamp, the employer must accept it as a receipt establishing both employment authorization and identity for 90 days. After 90-days, the employee must present either an EAD or a combination of a List B document and List C (an unrestricted social security card.)



Scenario Two: Asylee presents a Form I-94:
An employer must accept Form I-94 or Form I-94A with one of the stamps or notations below indicating asylee status:
- Asylum granted indefinitely
- 8 CFR 274a.12(a)(5)
- INA 208
This is a List C document that does not require/contain an expiration date. However, the asylee will need to present a List B identity document with this Form I-94.
*Decisions from immigration judges granting asylum are not acceptable.

For further assistance on training your company’s hiring personnel on all of the requirements of Form I-9 compliance, contact one of our immigration professionals at info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or call 562 612.3996.
Tags: Best Packaging I-9 Ruling, DOJ, I-9 Acceptable Documents, I-9 Anti-Discrimination Provision, I-9 Discrimination, I-9 Document Examination, I-9 for Refugees/Asylees, I-9 Over-Documentation, I-9 Training, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, OSC, Worksite Enforcement
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Uncategorized, USCIS | Comments Off on Form I-9 How To Guide: Employing Refugee/Asylee(s)
Friday, May 11th, 2012
By Timothy Sutton, Communications Editor | Immigration Compliance Group
 Amendments to The Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organization Act (RICO) in 1996 expose businesses to civil liability for knowingly hiring illegal workers. RICO was originally enacted to protect businesses from the influence of the mafia by allowing private enforcement of sanctions against violators of racketeering laws. Today, if a business employs illegal workers both (1) private individuals who are directly and adversely affected by loss or depression of wages due to employment of illegal workers and (2) businesses who are proximately harmed by a direct competitors employment of illegal workers may seek monetary sanctions including attorney’s fees under RICO. Simply, if you are employing illegal workers, your legally employed workers and your direct competitors may sue you for racketeering.
Amendments to The Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organization Act (RICO) in 1996 expose businesses to civil liability for knowingly hiring illegal workers. RICO was originally enacted to protect businesses from the influence of the mafia by allowing private enforcement of sanctions against violators of racketeering laws. Today, if a business employs illegal workers both (1) private individuals who are directly and adversely affected by loss or depression of wages due to employment of illegal workers and (2) businesses who are proximately harmed by a direct competitors employment of illegal workers may seek monetary sanctions including attorney’s fees under RICO. Simply, if you are employing illegal workers, your legally employed workers and your direct competitors may sue you for racketeering.
In Trollinger v. Tyson Foods, Inc., legally authorized workers filed a civil RICO class action against Tyson claiming the company and its recruiters had violated the INA by entering into an illegal hiring scheme to pay illegal aliens lower wages to increase profits. The workers claimed that their own wages had been depressed by Tyson’s immigration violations. Tyson prevailed after six long years of civil litigation because the plaintiff’s failed to establish a sufficient causation of their lost wages by Tyson’s hiring of illegal workers. However, this case set out the framework for employees to bring a lawsuit against their employer for hiring illegal workers under RICO.
Because the government holds private businesses accountable for enforcing immigration laws through I-9 compliance, E-verify and various Federal statutes, workplace compliance is essential to protecting your business. Businesses, not illegal workers are held accountable for fraudulent documents, misrepresentations of citizenship, and discriminatory hiring practices.
As “gatekeepers,” of immigration enforcement, employers have a de-facto duty to prevent illegal immigrants from securing employment. To ensure that your business is prepared for RICO lawsuits, ICE audits, and OSC hiring discrimination claims, contact one of our immigration professionals at info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or call 562 612.3996.
Our Employer Resource Center is very informative – check it out.
Tags: Employment Eligibility Verification, I-9 Form, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE Audits, ICE Investigation, Illegal Workers, Immigration Compliance Group, Legal Workforce, OSC, RICO Act, Undocumented Workers, Worksite Enforcement
Posted in I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News | Comments Off on I-9 Form: Can An Anti-Mafia Law Criminalize Your Legitimate Business?














 Amendments to The
Amendments to The