Posts Tagged ‘DOJ’
Friday, July 8th, 2016

This rule implements as an inflation adjustment fines for employing unauthorized workers for Form I-9 paperwork violations, and for immigration-related discrimination. These new fines increase the penalties from 35% to 96% depending on the nature and severity of the violation.
We encourage you to review your policies, procedures and your Form I-9 inventory. Remember, the key to defending any employment related investigation is to evidence that there is and has been a consistent pattern of responsible, good faith effort on the part of the employer in establishing a compliant workforce.
Refer here for the details.
Tags: DOJ, I-9 AUDIT, I-9 Compliance, I-9 Penalties, I-9/E-Verify, ICE, Immigration compliance, Legal Workforce, OSC, USCIS
Posted in DOJ, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, OSC, USCIS | Comments Off on DOJ issues interim final rule increasing fines 35-96% for employing unauthorized workers
Sunday, September 20th, 2015

Plain and simple, failing to comply with IRCA’s I-9 rules have, and are continuing at a rapid rate, to result in significant fines, loss of access to government contracts, an onslaught of negative publicity, business closure, criminal penalties and even imprisonment. Here are a few examples of recently settled cases in August 2015:
1) Creating discriminatory barriers for immigrants who have permission to work in the United States, $165 civil penalty with $50K in back pay:
http://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/justice-department-settles-discrimination-claim-against-louisiana-crane-construction
2) Requiring non-U.S. citizens, but not similarly-situated U.S. citizens, to present specific documentary proof of their immigration status to verify their employment eligibility, $200K civil penalty: http://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/justice-department-settles-immigration-related-discrimination-claim-against-nebraska-based
3) City of Eugene, OR improperly restricted law enforcement positions to U.S. citizens at the time of hire, even though no law, regulation, executive order or government contract authorized such a restriction. must pay a civil penalty, train its employees about the anti-discrimination provision of the INA and be subject to monitoring by the Justice Department for a period of three years!
http://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/justice-department-settles-citizenship-discrimination-claim-against-city-eugene-oregon
:::::::::::::::::::::
Immigration Compliance Group provides US inbound immigration services to individuals and employers throughout the USA and abroad. We specialize in business immigration and have a depth of experience in the IT, healthcare, arts, entertainment and sports industries, amongst others. Our services include complex business visas for investors, multinational managers, skilled professionals, outstanding individuals of high achievement (O-1, P visas, EB-1 and EB-2 Exceptional Ability cases) and PERM Labor Certification. We additionally provide employer compliance consulting services on proper I-9 (Employment Eligibility Verification) management, auditing, training, and work with our clients to develop a culture of immigration compliance. Our door is open for new clients — we extend a 20% discount on the first case with our firm. Contact us at info@immigationcompliancegroup.com or call 562 612.3996.
Tags: DOJ, Employer Compliance, Employoment Eligibility Verification, I-9 Audits, I-9 Form, I-9 Penalties, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OSC, Social Security Card, USCIS
Posted in DOJ, Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, OSC | Comments Off on Recent DOJ Worksite Enforcement Settlements that Shed Light on Form I-9 Employer Compliance
Thursday, August 16th, 2012
The Department of Justice Office of Public Affairs recently published a press release pertaining to the employment of two refugees resolving allegations that the company discriminated under the anti-discrimination provision of the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA), when it impermissibly delayed the start date of two refugees after requiring them to provide specific Form I-9 documentation. Best Packing’s violations occurred when they required the refugees to supply the company with additional Form I-9 verification documents in excess of the law. The claim alleged that other non-refugee employees were not required to supply documents other than state issued licenses and social security cards.
In two charges filed with the department, the refugees alleged that they were not allowed to begin employment until they produced unexpired, Department of Homeland Security-issued employment authorization documents, despite the fact that they initially presented sufficient documentation for employment eligibility verification purposes. The charging parties had presented unexpired state identification cards and unrestricted Social Security cards. The state ID’s and unrestricted SS cards were deemed insufficient proof of work authorization.
It is necessary for all those charged with Form I-9 processing at your organization to be very familiar with the list of acceptable documents and to have a thorough understanding of the fact that each employee has the right to present a list A document or a combination B plus C document as long as they are acceptable documents, appear to be genuine and represent the employee that is before you.
Under the settlement agreement, Best Packing agreed to pay $4,379 in back pay and comply with all the requirements of the INA. Understanding the Form I-9 requirements for verifying refugee/asylee(s) will prevent your company from falling victim to similar discriminatory hiring practices.
The process by which an employer is required to verify the employment eligibility of a refugee/asylee(s) when presented with documentation other than the above-referenced List B plus List C combination, can be a bit complicated. Let’s review this.
Asylees and Refugees are individuals seeking the protection of the United States due to persecution suffered in the home country based upon: race, religion, nationality, social group, or political ideology. These individuals are authorized to work in the US because of their immigration status. When presented with documentation of asylum or refugee status, it is advisable to be aware of the following in regard to examining the I-9 form and the documents presented:
SECTION 1:
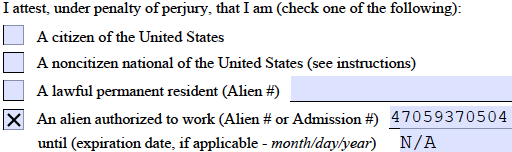
- The employee should check the “An alien authorized to work” box
- Write the I-94 or Alien Registration Number in the first space
- Write “N/A” in the second space, because their employment authorization does not expire
SECTION 2:
Acceptable Documents are I-94, I-766, or their Employment Authorization Document also known as an EAD card
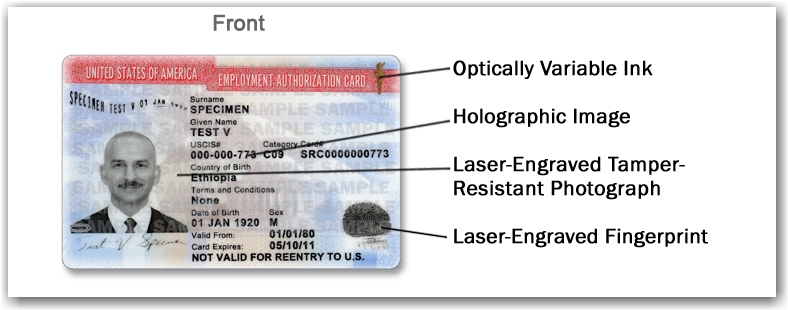
NOTE: this section presents two different scenarios that require strict attention to time restrictions and combinations of required documents to be presented in order to comply with the USCIS regulations. To complete this section choose from the applicable scenarios below:
Scenario One: Refugee presents a Form I-94:
When presented with a Form I-94 containing an unexpired refugee admission stamp, the employer must accept it as a receipt establishing both employment authorization and identity for 90 days. After 90-days, the employee must present either an EAD or a combination of a List B document and List C (an unrestricted social security card.)



Scenario Two: Asylee presents a Form I-94:
An employer must accept Form I-94 or Form I-94A with one of the stamps or notations below indicating asylee status:
- Asylum granted indefinitely
- 8 CFR 274a.12(a)(5)
- INA 208
This is a List C document that does not require/contain an expiration date. However, the asylee will need to present a List B identity document with this Form I-94.
*Decisions from immigration judges granting asylum are not acceptable.

For further assistance on training your company’s hiring personnel on all of the requirements of Form I-9 compliance, contact one of our immigration professionals at info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or call 562 612.3996.
Tags: Best Packaging I-9 Ruling, DOJ, I-9 Acceptable Documents, I-9 Anti-Discrimination Provision, I-9 Discrimination, I-9 Document Examination, I-9 for Refugees/Asylees, I-9 Over-Documentation, I-9 Training, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, OSC, Worksite Enforcement
Posted in Employer Compliance, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News, Uncategorized, USCIS | Comments Off on Form I-9 How To Guide: Employing Refugee/Asylee(s)
Sunday, July 1st, 2012
By: Timothy Sutton, Communications Editor
In the USDOJ published decision United States v. Four Seasons Earthworks, ICE made it clear that with respect to form I-9 compliance, late is not any better than never. Four Seasons failed to pass an ICE audit that found incomplete form I-9 List A and List C information. The company asserted they obtained every employee’s social security number and maintained supporting documents (like military IDs and birth certificates) necessary to verify employment eligibility. ICE’s response was terse, “Late production nevertheless does not absolve the respondent from liability.”
Securing qualified employees can be stressful. Once a worthy recruit is hired, employers may be anxious to have the new-hire begin working even before they secure the required documentation to complete the I-9 form. Improper documentation constitutes a violation under the INA. In it’s investigation of Four Seasons Earthworks, the ICE Forensic Auditor calculated penalties based upon the following formula:
 Number of Violations divided by the total number of current & former employees up to inspection date = % of base fine
Number of Violations divided by the total number of current & former employees up to inspection date = % of base fine
Additionally, 5% increases for bad-faith or serious violations are tacked on to penalties. The number of undocumented workers, the size of a business, and previous violations are also considerations that increase penalties.
Thankfully, an employer’s good faith attempt to comply with obligations can influence a penalty reduction. ICE views hiring violations on a continuum, recognizing violations vary in severity. If your company finds itself in a similar situation with employees who are not properly documented, hiring immigration compliance professionals may greatly reduce your chances of incurring audit-initiated penalties. Contact us for support in planning and implementing legally sound solutions to protect your company’s future: 562 612.3996 | info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com.
Tags: DOJ, Four Seasons Earthworks, I-9 AUDIT, I-9 Penalties, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, ICE Audit, Immigration News, Legal Workforce, OCAHO, Undocumented Workers
Posted in DOJ, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Immigration News | Comments Off on I-9 Compliance: Too Much To Ask?
Friday, January 6th, 2012
 The Justice Department has reached a settlement agreement with University of California San Diego Medical Center for $115,000 (one of the higher civil penalties we’ve seen) for a complaint filed on Dec. 6, 2011, alleging that the medical center failed to comply with proper I-9 Form employment eligibility verification processes for non-citizens who are authorized to work in the United States.
The Justice Department has reached a settlement agreement with University of California San Diego Medical Center for $115,000 (one of the higher civil penalties we’ve seen) for a complaint filed on Dec. 6, 2011, alleging that the medical center failed to comply with proper I-9 Form employment eligibility verification processes for non-citizens who are authorized to work in the United States.
Specifically, the DOJ’s complaint alleged that UCSD medical center engaged in a pattern of subjecting newly hired non-U.S. citizens to excessive demands for documents issued by the Department of Homeland Security in order to verify their employment eligibility, but did not require the same of US citizens. The Immigration and Nationality Act’s (INA) anti-discrimination provision prohibits employers from placing unfair documentary burdens on work-authorized employees during the hiring and employment eligibility verification process based on their citizenship status or national origin. Clearly put, it is illegal to discriminate against work authorized individuals. You simply cannot specify which documents are to be presented. This is considered document abuse.
The medical center has taken appropriate action to ensure compliance with INA’s anti-discrimination provision and has received Department of Homeland Security/U.S. Immigration & Customs Enforcement (ICE) training on the proper use of work authorization documents. They have also agreed to work with the DOJ to ensure compliance with proper I-9 processes across all University of California campuses, medical centers and facilities.
Under the terms of the settlement agreement, the medical center agrees to implement new employment eligibility verification policies and procedures that treat all employees equally regardless of citizenship status. In addition, the medical center has agreed to pay a civil penalty of $115,000, conduct supplemental training of its human resources personnel on their responsibilities to avoid discrimination in the employment eligibility verification process and work with the department to ensure compliance with proper employment eligibility verification processes across all University of California campuses, medical centers and facilities.
Heightened Enforcement Continues
During the past few years, we have seen unprecedented enforcement and legislative activity relating to Form I-9 and E-Verify worksite compliance. Since fiscal year 2009, ICE has audited more than 6,000 employers, debarred 441 companies and individuals, and imposed more than $76 million in financial sanctions. We have also seen an unprecedented increase in the number of enforcement actions brought about by the Department of Justice (DOJ) for discrimination in the I-9 process. The Office of Special Counsel (OSC) has robustly prosecuted claims of discrimination in the I-9 process resulting in fines and penalties against employers, as well as back pay to injured parties.
What employers need to know
You just cannot presume that the employees charged with managing your I-9 program are compliant with the law and adhering to anti-discrimination rules and regulations. If you are not training your employees, then you are turning a blind eye to establishing a compliant workforce, the consequences of which today are severe and expensive – not to mention the bad press that accompanies such an investigation.
Employers cannot request specific documents (such as a green card), reject documents that reasonably appear to be genuine and relate to the employee presenting them, request that employees produce more documents than are required or treat groups of applicants differently when completing the I-9 form. You must examine ANY acceptable document from List A that appears to be genuine and that relates to the worker, or a combination List B plus a List C document, regardless of whether or not
Let’s re-visit ICE’s list of best practices that include the following as a reminder to employers:
- Use E-Verify,
- Use the Social Security Number Verification Service (SSNVS) for wage reporting purposes
- Establish a written hiring and employment eligibility verification policy.
- Establish an internal compliance and training program related to the hiring and employment verification process
- Require the I-9 process to be conducted only by individuals who have received appropriate training and include a secondary review as part of each employee’s verification to minimize the potential for a single individual to subvert the process.
- Arrange for annual I-9 audits by an external auditing firm or a trained employee not otherwise involved in theI-9 process.
- Establish a protocol for responding to letters or other information received from federal and state government agencies indicating that there is a discrepancy between the agency’s information and the information provided by the employer, such as SSA “No-Match” letters
- Establish and maintain appropriate policies, practices and safeguards to ensure that authorized workers are not treated differently with respect to hiring, firing, or recruitment or referral for a fee or during the Form I-9, E-Verify or SSNVS processes because of citizenship status or national origin.
- Maintain copies of any documents accepted as proof of identity and/or employment authorization for all new hires.
For more, refer to:
1) DOJ Press Release
2) DOJ Press Release on one of the largest settlements against a major healthcare system
3) Our list of services and solutions
__________________
About Immigration Compliance Group
For those of you who may be first time readers, Immigration solutions provides US and Canadian business immigration services to employers and individuals and additionally provides a full range of I-9 employment eligibility compliance services for employers that require I-9 audits, training, and compliance policy development.
Tags: DOJ, E-Verify, Employer Compliance, Employment Eligibility Verification, Healthcare, I-9 Audits, I-9 Discrimination, I-9 Fines, I-9 management, I-9 News, I-9 Penalties, I-9 Training, I9 Document Abuse, ICE, Immigration Compliance Group, Legal Workforce, OSC, SSA No-Match, UC San Diego Medical Center
Posted in DOJ, Healthcare, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, Staffing Agencies | Comments Off on Form I-9 Discrimination | CA University Medical Center Pays $115,000
Thursday, December 29th, 2011
Here is another example of one of the major blunders made by employers in 2011 which is to require specific work authorization documents (permanent resident cards or employment authorization card) of non-US citizen employees rather than permitting them to choose from the list of acceptable documents on the I-9 form.
The Justice Department announced today that it reached a settlement with BAE Systems Ship Repair Inc., a leading provider of ship repair services, to settle allegations that its subsidiary, BAE Systems Southeast Shipyards Alabama LLC, engaged in a pattern or practice of discrimination by imposing unnecessary and additional document requirements on newly hired permanent residents (green-card holders) when establishing their eligibility to work in the USA by requiring them to present Permanent Resident Cards, a/k/a/ “green-cards,” as a condition of employment.
The investigation was initiated after BAE Southeast Alabama suspended a lawful permanent resident even though he had presented valid documents sufficient under the Immigration and Nationality Act (INA) to establish his work authorization on three separate occasions.
BAE agreed to pay a fine of $53,900. The lawful permanent resident who was suspended was previously reinstated and fully compensated by BAE. BAE agreed to ensure that the employment eligibility verification policies and procedures of all its subsidiaries comply with the law, to train its human resources personnel about employers’ responsibilities to avoid discrimination in the employment eligibility verification process, and to produce Forms I-9 for inspection for three years. We cannot emphasize enough the importance of employers with subsidiary companies and multiple jobsite locations establishing written, uniform policies and procedures concerning employment eligibility compliance matters. We also recommend that an I-9 Compliance Manager be appointed to oversee adherence to your compliance standard operating procedures for all subsidiary companies at all locations.
The INA requires employers to treat all authorized workers in the same manner during the employment eligibility verification process, regardless of their national origin or citizenship status. Employees may choose which document(s) they want to present from the list of acceptable documents. Employers must accept any document from List A or combination of documents (one from List B and one from List C) as long as it the documents reasonably appear on their face to be genuine and to relate to the person presenting them. To act in any other manner can be an unfair immigration related employment practice in violation of the anti-discrimination provision of the INA.
We frequently are asked: If an employee writes down an Alien Number or Admission Number when completing Section 1 of the I-9 form, may I ask to see a document with that number? The answer to this, based upon the above, is “no”. It is your responsibility to ensure that your employees fully complete Section 1; however, the employee is not required to present a specific document in order to complete this section. When the employer completes Section 2, you may not ask to see a document with the employee’s Alien Number or Admission Number or otherwise specify which document(s) an employee may present.
Should you wish to communicate with our office regarding audits, training and policy development, please email us at info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or call 562 612.3996. Please sign up for our free news and visit our Blog and employer compliance resource center at: www.I-9Audits.com
Tags: DOJ, E-Verify, Employer Compliance, Employment Eligibility Verification, I-9 Audits, I-9 Compliance, I-9 Discrimination, I-9 Fines, I-9 Form, I-9 management, I-9 process, I-9 Training, I9, Legal Workforce, NOI, Non-US Citizens, SSA No-Match
Posted in DOJ, I-9/E-Verify News | Comments Off on I-9 Form Compliance for Non-US Citizen Employees
Thursday, December 15th, 2011
OSC is conducting a free, live webinar series on Worksite Discrimination. If you’re a worker or worker advocate, they have a monthly worker/advocate track webinar. Employers/HR professionals are invited to join their monthly OSC Employer Training webinar. The webinars are conducted live from OSC’s headquarters in Washington, DC. You might want to check this out.
Here is a link to the OSC Powerpoint used in today’s Employer Worksite Discrimination Webinar. It was a very informative and well done presentation.
Should you wish to discuss how best to implement policies and procedures that will enhance your compliance program, we’d be glad to hear from you: info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com or 562 612.3996.
Tags: Citizenship Discrimination, DOJ, I9 audits, I9 compliance, I9 form, ICE, ICE investigations, Legal Workforce, National Origin Discrimination, NOI, OSC, Worksite Discrimination, Worksite Enforcement
Posted in I-9/E-Verify News, ICE | Comments Off on OSC Worksite Discrimination Webinars
Monday, November 28th, 2011
We recommend that every employer read this brochure very carefully. As it clearly states, the: “OSC vigorously investigates and prosecutes such claims of discrimination. Employers found to be engaging in discriminatory activity may be required to pay civil penalties and any appropriate back pay to injured parties.”
The case examples provided with accompanying fines mentioned in the brochure are excellent studies for HR professionals that deal with I-9s on a daily basis. We highly recommend that you print this out and add it to your M-274 Employer Handbook. Make sure that all HR representatives, HR and hiring managers involved with the I-9 process has a copy of this brochure.
Should you have any questions, please feel free to contact our office at: info@immigrationcompliancegroup.com, or by phone 562 612.3996.
Tags: DOJ, form I-9, I-9 Audits, I-9 Compliance, I-9 Discrimination, I-9 Fines, I-9 management, I-9 process, ICE, Immigration Compliance Group, Immigration Discrimination, Legal Workforce, National Origin Discrimination, OSC
Posted in I-9/E-Verify News, ICE | Comments Off on I-9 Form: OSC Releases Brochure on Immigration & National Origin Discrimination
Saturday, September 10th, 2011
The Department of Justice (“DOJ”) reported that it had reached a settlement with Brand Energy and Infrastructure Services and its subsidiary, Industrial Services LLC (ISI) on July 21, 2011. The DOJ reports that Industrial Services engaged in a pattern and practice of discrimination while completing Form I-9 on its non-citizen workers requiring specific employment documentation beyond what was required by law.
The investigation was prompted after a work-authorized immigrant lost his job when he could not comply with ISI’s request to provide specific employment documentation beyond what was required by law. Further investigation revealed that ISI’s Prairieville, LA office required all newly hired non-U.S. citizens to present documents issued by the Department of Homeland Security upon hire. The company did not require U.S. citizens to present any particular documents.
ISI has agreed to pay $43,560 in civil penalties and $7,200 in back pay, plus interest, to the injured party. Brand and ISI have also agreed to monitoring provisions, as well as training for their human resources personnel.
What employers need to know: You just cannot presume that the employees charged with managing your I-9 program are compliant with the law and adhering to anti-discrimination rules and regulations if you’re turning a blind eye to your compliance issues, the consequences of which today are severe and expensive – not to mention the bad press that accompanies such an investigation. Employers must accept ANY acceptable document from List A that appears to be genuine and that relates to the worker, or a combination List B plus a List C document. Additionally, employers are not to require more documentation than what is itemized on the List of Documents for Form I-9.
Let’s re-visit ICE’s list of best practices that include the following as a reminder to employers:
- Internal compliance & training program
- Polices/procedures safeguard against discrimination incl. training
- Require I-9 process only by those trained
- Secondary review for each I-9
- Annual I-9 audits by external auditing firm or trained person not involved in I-9 process
- Protocol to respond to tips/information/constructive knowledge
- Maintain copies of documents
- Participation in E-Verify/SSNVS
We are available to assist you with your compliance needs. Please visit our Employer Resource Center and contact us should you wish to discuss our services and solutions.
Tags: Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), DOJ, E-Verify, Employer Compliance, I-9 Audits, I-9 Compliance, I-9 Discrmination, I-9 Fines, I-9 Form, I-9 Training, ICE, Legal Workforce, SSA No-Match, USCIS, Worksite Enforcement
Posted in Department Of Homeland Security (DHS), DOJ, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE, USCIS | Comments Off on I-9 Form: Employer Fined for Discrimination
Monday, August 29th, 2011
Kinro Mfg. a subsidiary of Kinro Inc., which is wholly owned by White Plains, N.Y.-based Drew Industries Inc., has been fined a $25,000 civil penalty and $10,000 in back pay to the injured party for engaging in a pattern/practice of discrimination against work-authorized non-citizens in the employment eligibility verification process. The company is a manufacturer of components for recreational vehicles and manufactured homes.
Kinro has also agreed to train its human resources personnel about employers’ responsibilities to avoid discrimination in the employment eligibility verification process, to produce Forms I-9 for inspection and to provide periodic reports to the DOJ for one year.
According to the department’s findings, the company subjected newly hired non-U.S. citizens to excessive demands for documents issued by the Department of Homeland Security in order to verify their employment eligibility, but did not require U.S. citizens to show any specific documentation . The charging party, a lawful permanent resident, filed his charge of discrimination after he was required to provide additional proof of his employment eligibility not required by law before he could begin work at the company.
View Press Release
Tags: DOJ, EMPLOYMENT ELIGIBILITY, I-9 Audits, I-9 Civil Penalties, I-9 Compliance, I-9 Fines, I-9 Penalties, ICE, Legal Workforce, NOI, Worksite Enforcement
Posted in DOJ, I-9/E-Verify News, ICE | Comments Off on I-9 Fines: DOJ Settles with Kinro Mfg on I-9 Employment Discrimination